LeetCode 솔루션 분류
[7/22] 86. Partition List
본문
Medium
3949529Add to ListShareGiven the head of a linked list and a value x, partition it such that all nodes less than x come before nodes greater than or equal to x.
You should preserve the original relative order of the nodes in each of the two partitions.
Example 1:
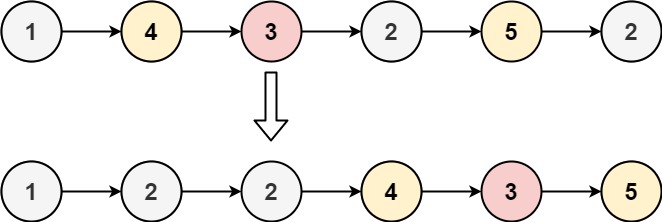
Input: head = [1,4,3,2,5,2], x = 3 Output: [1,2,2,4,3,5]
Example 2:
Input: head = [2,1], x = 2 Output: [1,2]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 200]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100-200 <= x <= 200
Accepted
366,386
Submissions
745,447
관련자료
-
링크
댓글 1
학부유학생님의 댓글
- 익명
- 작성일
Runtime: 38 ms, faster than 90.25% of Python3 online submissions for Partition List.
Memory Usage: 13.9 MB, less than 31.57% of Python3 online submissions for Partition List.
Memory Usage: 13.9 MB, less than 31.57% of Python3 online submissions for Partition List.
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def partition(self, head: Optional[ListNode], x: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head or not head.next: return head
sub_head = head
sub_prev = dummy = ListNode(0, head)
while sub_head and sub_head.val < x:
sub_head = sub_head.next
sub_prev = sub_prev.next
curr = sub_head
prev = sub_prev
while curr:
if curr.val < x:
tmp_next = curr.next
sub_prev.next = curr
curr.next = sub_head
sub_prev = sub_prev.next
prev.next = tmp_next
curr = tmp_next
else:
curr = curr.next
prev = prev.next
return dummy.next










