LeetCode 솔루션 분류
[5/17] 1379. Find a Corresponding Node of a Binary Tree in a Clone of That Tree
본문
[LeetCode 시즌 3] 2022년 5월 17일 문제입니다.
https://leetcode.com/problems/find-a-corresponding-node-of-a-binary-tree-in-a-clone-of-that-tree/
1379. Find a Corresponding Node of a Binary Tree in a Clone of That Tree
Medium
9151189Add to ListShareGiven two binary trees original and cloned and given a reference to a node target in the original tree.
The cloned tree is a copy of the original tree.
Return a reference to the same node in the cloned tree.
Note that you are not allowed to change any of the two trees or the target node and the answer must be a reference to a node in the cloned tree.
Example 1:
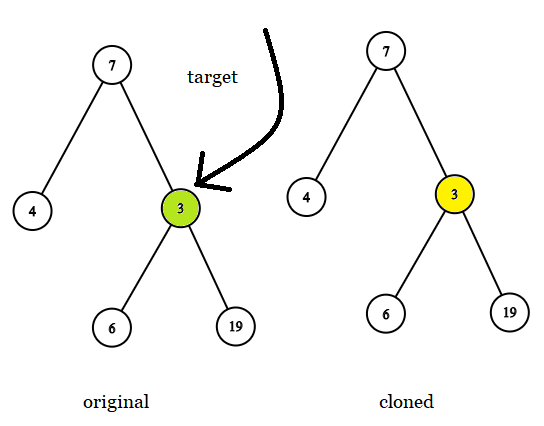
Input: tree = [7,4,3,null,null,6,19], target = 3 Output: 3 Explanation: In all examples the original and cloned trees are shown. The target node is a green node from the original tree. The answer is the yellow node from the cloned tree.
Example 2:
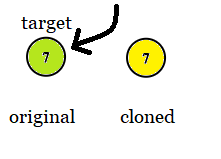
Input: tree = [7], target = 7 Output: 7
Example 3:
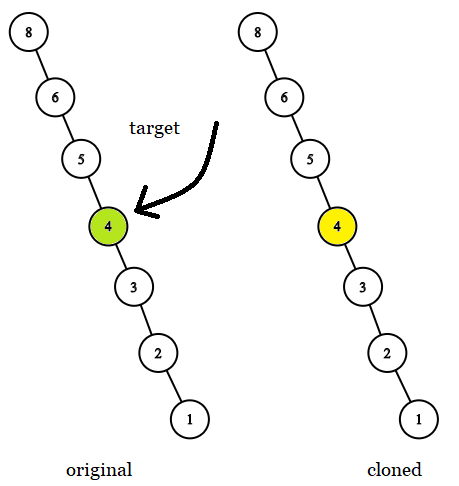
Input: tree = [8,null,6,null,5,null,4,null,3,null,2,null,1], target = 4 Output: 4
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the
treeis in the range[1, 104]. - The values of the nodes of the
treeare unique. targetnode is a node from theoriginaltree and is notnull.
Follow up: Could you solve the problem if repeated values on the tree are allowed?
관련자료
-
링크
댓글 3
mingki님의 댓글
- 익명
- 작성일
C++
Runtime: 604 ms, faster than 68.91% of C++ online submissions for Find a Corresponding Node of a Binary Tree in a Clone of That Tree.
Memory Usage: 163.9 MB, less than 81.24% of C++ online submissions for Find a Corresponding Node of a Binary Tree in a Clone of That Tree.
Runtime: 604 ms, faster than 68.91% of C++ online submissions for Find a Corresponding Node of a Binary Tree in a Clone of That Tree.
Memory Usage: 163.9 MB, less than 81.24% of C++ online submissions for Find a Corresponding Node of a Binary Tree in a Clone of That Tree.
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* getTargetCopy(TreeNode* original, TreeNode* cloned, TreeNode* target) {
if (!original || !cloned || !target) return NULL;
if (original == target) return cloned;
return (TreeNode*) (
(long)getTargetCopy(original->left, cloned->left, target) |
(long)getTargetCopy(original->right, cloned->right, target)
);
}
};austin님의 댓글
- 익명
- 작성일
Runtime: 518 ms, faster than 91.55% of C++ online submissions for Find a Corresponding Node of a Binary Tree in a Clone of That Tree.
Memory Usage: 164 MB, less than 58.30% of C++ online submissions for Find a Corresponding Node of a Binary Tree in a Clone of That Tree.
Memory Usage: 164 MB, less than 58.30% of C++ online submissions for Find a Corresponding Node of a Binary Tree in a Clone of That Tree.
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* getTargetCopy(TreeNode* original, TreeNode* cloned, TreeNode* target) {
if (!cloned || original == target) return cloned;
auto ret = getTargetCopy(original->left, cloned->left, target);
return ret ? ret : getTargetCopy(original->right, cloned->right, target);
}
};나무토끼님의 댓글
- 익명
- 작성일
class Solution:
def getTargetCopy(self, original: TreeNode, cloned: TreeNode, target: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
def inorder(o, c):
if o:
inorder(o.left, c.left)
if o is target:
self.ans = c
inorder(o.right, c.right)
inorder(original, cloned)
return self.ans









